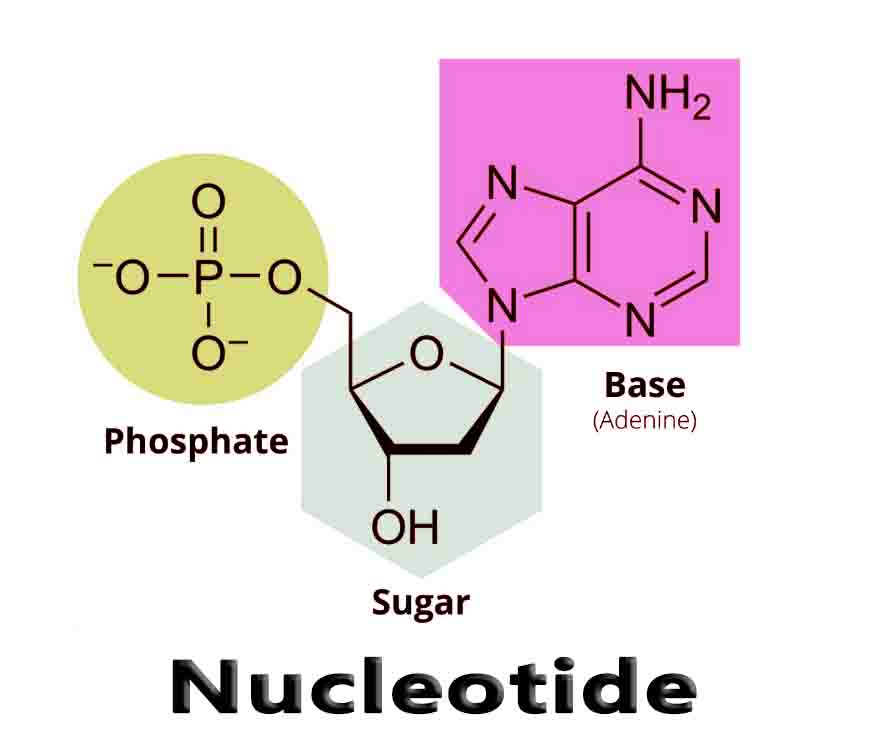
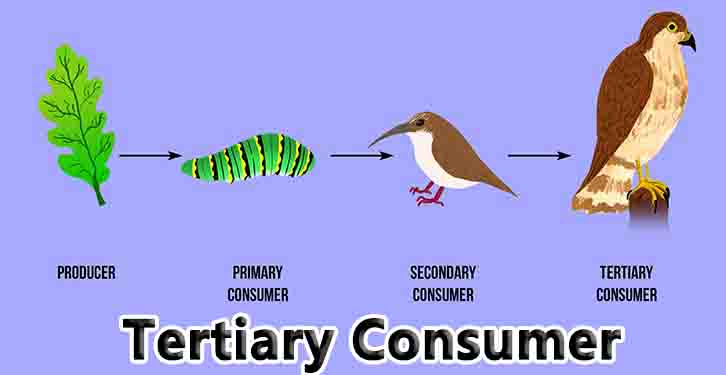
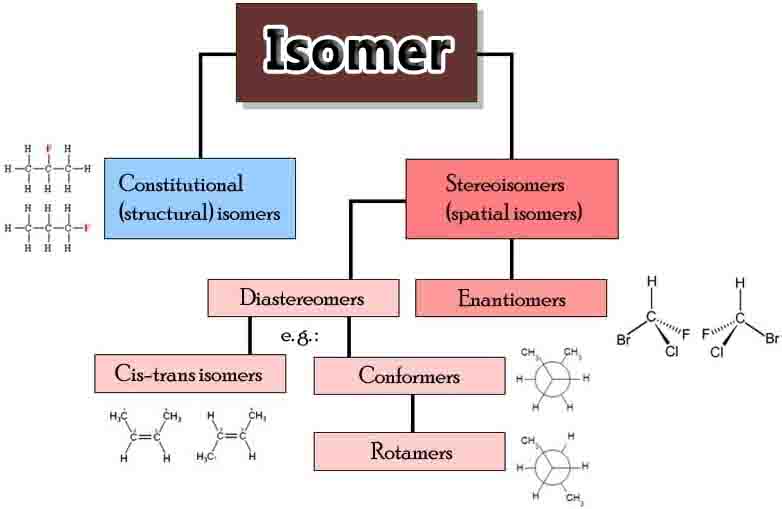
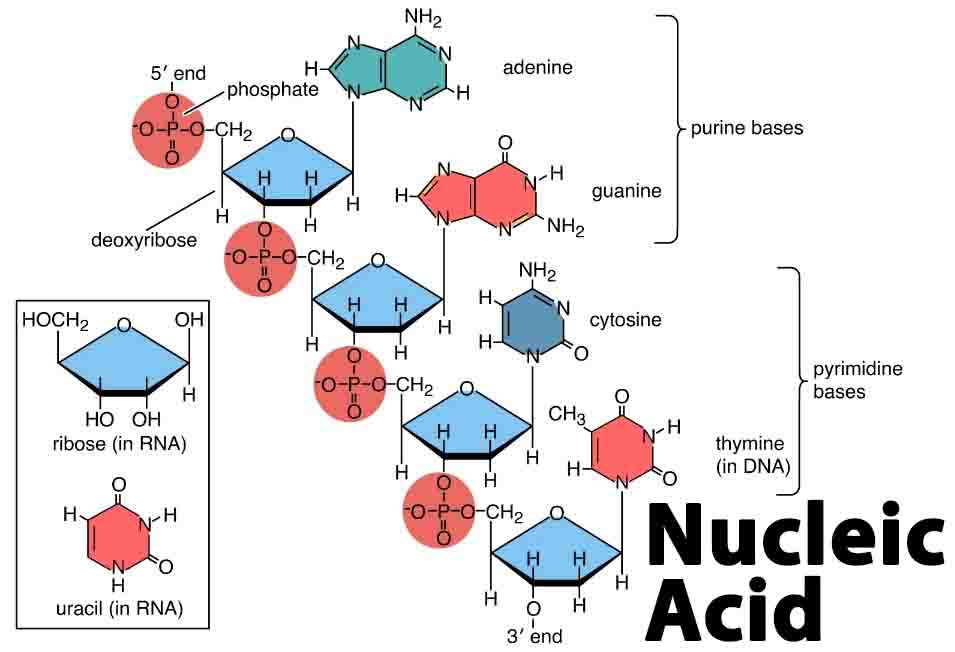
Species
Species Definition A species is a group of organisms that share a genetic heritage, are able to interbreed, and to create offspring that are also fertile. Different species are separated from each other by reproductive barriers. These barriers can be geographical, such as a mountain range separating two populations, or genetic barriers that do not … Read more