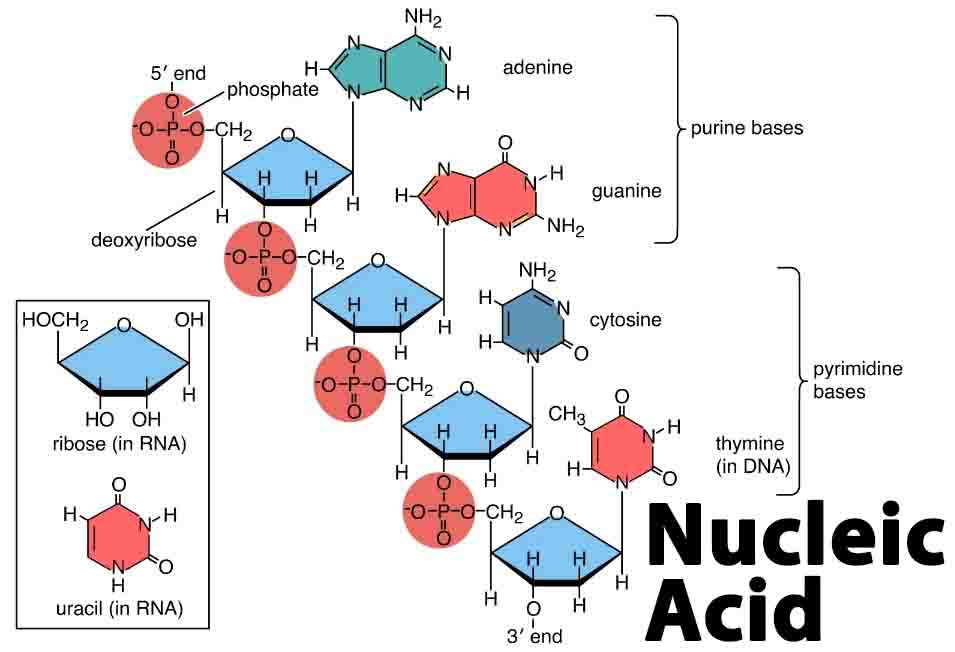
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition In the absence of oxygen or electron transport chains, fermentation refers to the conversion of organic molecules (normally glucose) into acids, gases, or alcohol. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is generated in glycolysis via fermentation pathways that regenerate the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Through glycolysis, fermentation yields only two molecules of ATP per glucose … Read more