In the eons of evolutionary time, organisms have differentiated themselves in recognizable ways. Divergent evolution and convergent evolution are two of these patterns. It provides evidence for the theory of evolution by showing how organisms have responded to natural selection.
Convergent Evolution
A convergence of evolution occurs when different species have evolved similar traits in response to a similar environment or pressure. In order to swim fast through the water, sharks and dolphins have streamlined, bullet-like shapes.
Sharks, however, are fish, while dolphins are mammals, and their evolutionary paths are very different. It is powerful evidence for natural selection that organisms without a common ancestor can evolve in similar ways.
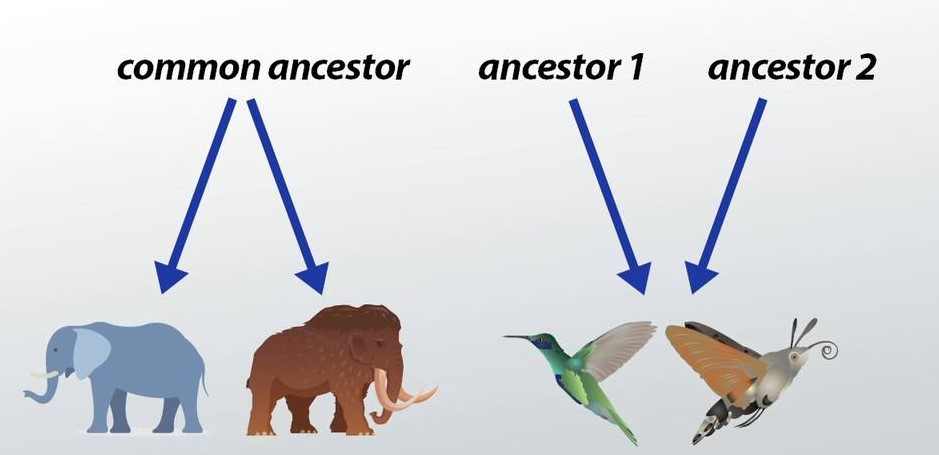
Divergent Evolution
As the name implies, divergent evolution shows how species can change slightly over time and separate (diverge) into new forms. For example, in vertebrates like pigs, birds, monkeys and whales, the forelimbs have the same general sets of bones, but they have been modified over time so the animals can use their forelimbs in very different ways.
Divergent evolution is studied on a larger scale such as how the current diversity of life on Earth evolved from the first living cells, to a smaller scale where natural selection caused humans and apes to evolve from a common ancestor.
Differences Between Convergent and Divergent Evolution
Three main differences between convergent and divergent evolution are:
- Convergent evolution shows how species have evolved separately but have similar (analogous) structures. Divergent evolution demonstrates how species can have common (homologous) anatomical structures which have evolved for different purposes.
- Convergent evolution happens in organisms that are not closely related while divergent evolution is observed in organisms that are closely related.
- The relationship between the analogous structures in different species that evolved through convergent evolution can be less distinct compared to the homologous structures seen in divergent evolution which have the same basic structural plan.